
The developers of the Rhadamanthys information-stealing malware have recently released two major versions to add improvements and enhancements across the board, including new stealing capabilities and enhanced evasion.
Rhadamanthys is a C++ information stealer that first emerged in August 2022, targeting email, FTP, and online banking service account credentials.
The stealer is sold to cybercriminals via a subscription model, so it is distributed to targets using a variety of channels, including malvertizing, laced torrent downloads, emails, YouTube videos, and more.
Although it initially didn't receive much attention in the crowded info-stealers market, Rhadamanthys continued to improve, building upon its modular nature to add new features as needed.
Researchers at Check Point have looked into the two latest versions of Rhadamanthys and reported the addition of numerous changes and features that expand its stealing capabilities and spying functions.
Actively developed malware
Check Point analyzed Rhadamanthys version 0.5.0 and reports that it introduced a new plugin system that allows higher levels of customization for specific distribution needs.
Plugins could add a diverse range of capabilities to the malware while allowing cybercriminals to minimize their footprint by only loading those they need in each case.
The new plugin system indicates a shift towards a more modular and customizable framework as it allows threat actors to deploy plugins tailored to their targets, counteracting security measures identified during recon stages or exploiting specific vulnerabilities.
A plugin bundled with Rhadamanthys is 'Data Spy,' which can monitor for successful login attempts to RDP and capture the victim's credentials.
The 0.5.0 release also brought improved stub construction and client execution process, fixes on the system that targets cryptocurrency wallets, and fixes on the Discord token acquisition.
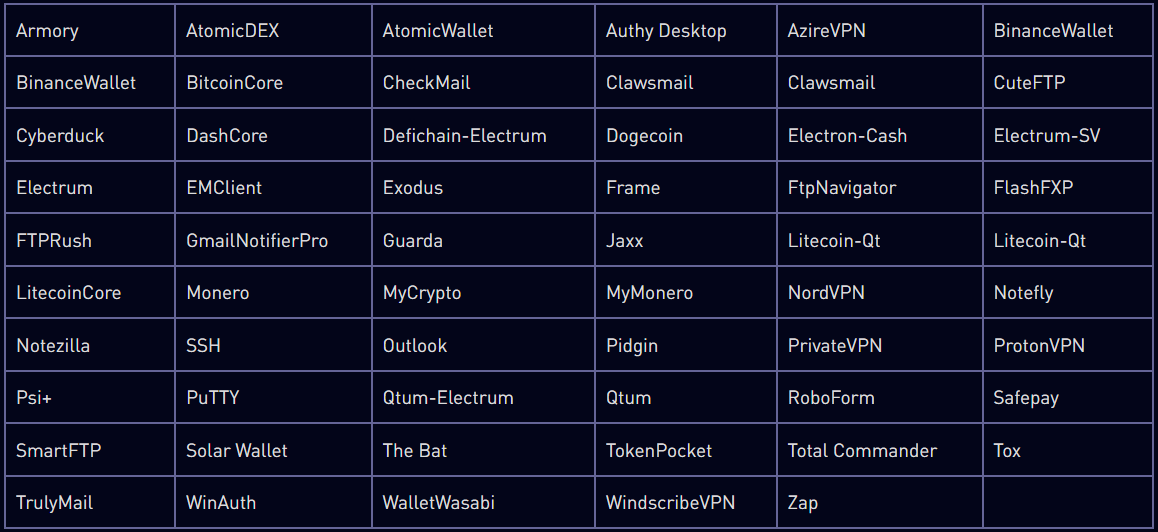
Other notable improvements include enhanced data stealing from browsers, updated search settings on the user panel, and an option to modify Telegram notifications.
Check Point notes that the malware loader has been rewritten to include anti-analysis checks, an embedded configuration, and a package with modules for the next stage (XS1).
Further analysis revealed the existence of the following modules loaded by XS1, five of which are new in Rhadamanthys version 0.5.0 and focus on evasion.
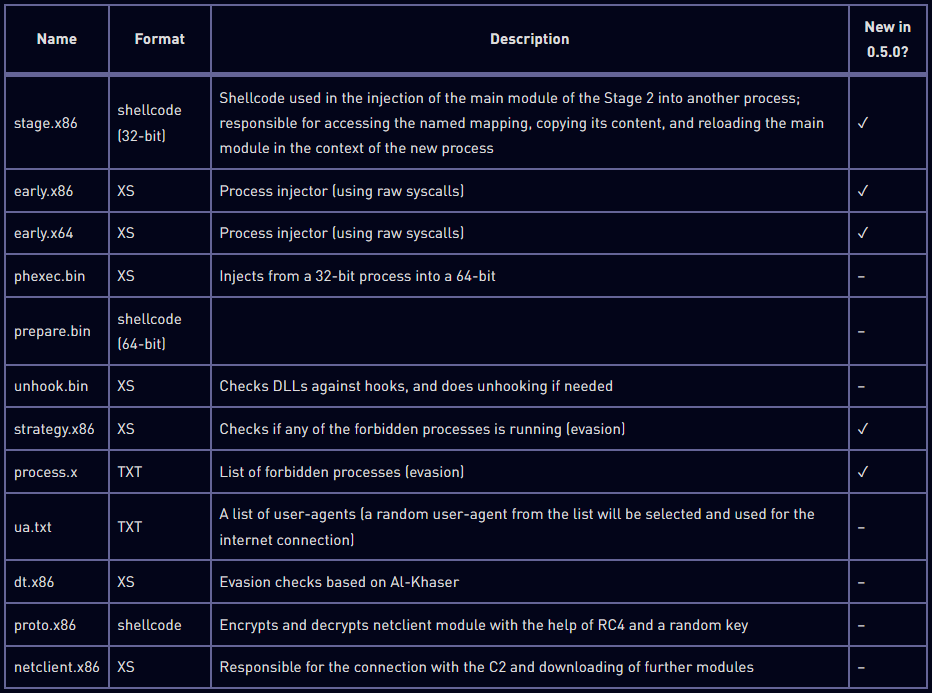
The XS1 loader unpacks those modules and establishes communication with the C2 (command and control) server, from where it receives and launches additional modules, including passive and active stealers.
Passive stealers are less intrusive info-stealing components that search through directories, monitor applications for sensitive data exchange, user entries, etc.

Active stealers are more invasive and involve keylogging, screen capturing, and code injection into running processes to exfiltrate as much data as possible.
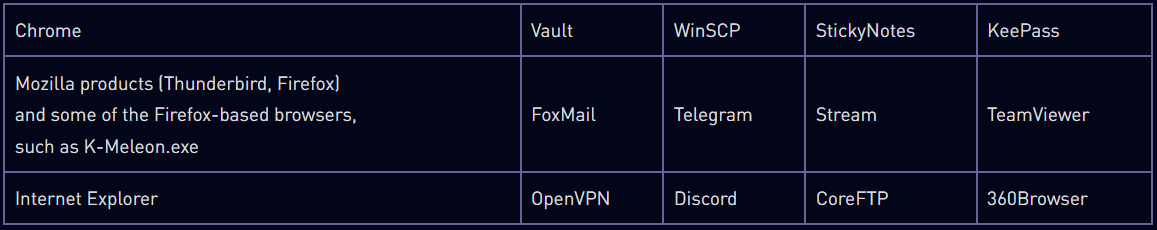
While Check Point's analysis of version 0.5.0, Rhadamanthys operators released version 0.5.1, which is a sign of very active development.
Check Point didn't have the chance to dive deep into the new version of the info-stealer, but the new features announced by the cybercriminals are impressive, even if not confirmed yet.
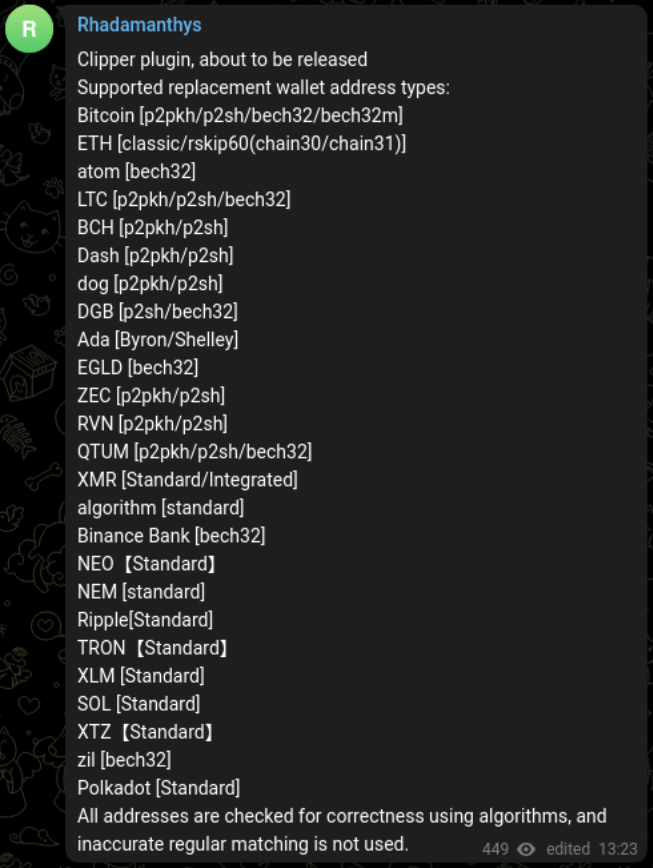
In short, 0.5.1 introduces:
- New Clipper plugin, that modifies clipboard data to divert crypto payments to the attacker.
- Telegram notification options to exfiltrate the wallet crack and seed in the exfiltrated ZIP
- Ability to recover deleted Google Account cookies (first reported here)
- Ability to evade Windows Defender, including cloud protection, by cleaning its stub.
The development of Rhadamanthys is moving quickly, with each new version adding features that make the tool more formidable and more inviting to cybercriminals.
It would not be surprising to find threat actors switching to Rhadamanthys as its development evolves.



Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now